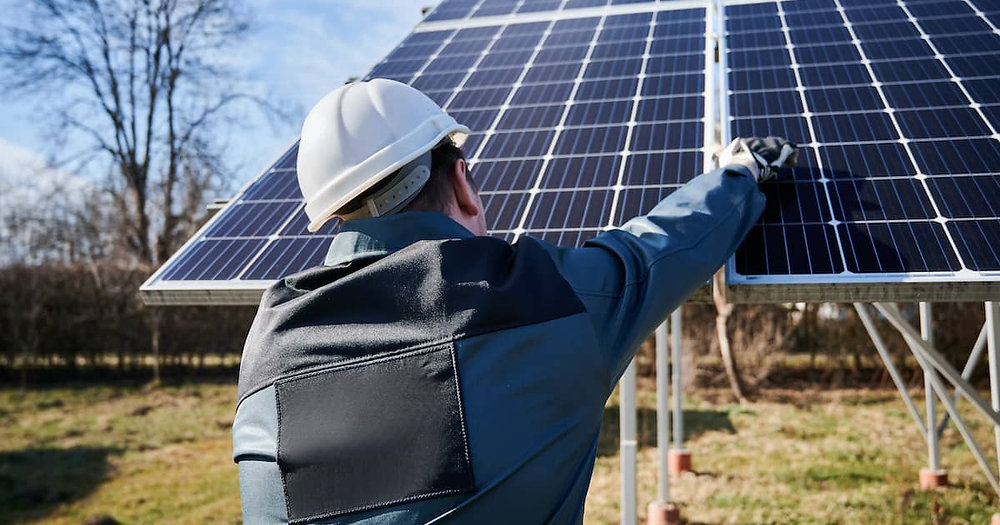
For homeowners with roofs that aren’t ideal for solar—due to shading, poor orientation, or structural concerns—ground mount solar design offers a high-performance alternative. Ground mounted solar panels can be positioned for maximum sun exposure, optimizing tilt and orientation to boost energy production and ROI.
While ground mounts provide greater flexibility, they require careful engineering and site preparation. Soil conditions dictate whether driven posts, helical piles, or ballast foundations are best, and longer wiring runs add complexity. Though ground mount solar systems typically have higher upfront costs, their superior efficiency and adaptability make them a strong long-term investment.
Offering ground mounts may increase your pool of potential solar energy customers and result in more satisfied customers. Sometimes, it can boost the output of the solar energy system, therefore boosting the return on investment. Some homeowners might want a solar tracking system on their array to increase energy production, making a ground mount essential. Unfortunately, ground mounts are often more complicated to engineer and install, especially for specific soil types.
To move projects forward smoothly, GreenLancer offers solar plan sets, engineering stamps, and engineering reviews—critical for permitting and system approval. We have more than a decade of experience solving solar engineering challenges for solar projects. Create a free account to start shopping GreenLancer solar solutions.
What Are Ground Mounted Solar Panels?
Ground mounted solar panels provide greater design flexibility than rooftop systems, allowing homeowners to install solar arrays in optimal locations for maximum sun exposure. Ground mount solar design is particularly beneficial for properties with ample open space, making it a popular choice for rural homes and farms. However, even suburban and urban properties with suitable yard space can accommodate ground-mounted systems.
For properties with limited space, solar panel mounting solutions can integrate with existing structures. Solar carports and solar trellises serve dual purposes—providing shade while supporting PV modules to generate electricity. Solar carports can protect vehicles from the elements, while a solar trellis installed on the south side of a home can provide shade for outdoor spaces while maximizing energy production.
Whether standalone or integrated into structures, ground mount solar systems require careful engineering to ensure structural stability, proper tilt, and efficient energy generation.
Three Types Of Ground Mounted Solar Panel Systems
Ground mount solar design offers three primary configurations: standard-mounted panels, pole-mounted panels, and solar carports. Each option has unique engineering and site preparation considerations. Let’s explore your options.
Standard Ground Mounted Solar Panels
This approach uses metal framing secured with ground anchors, such as concrete piers, ballasts, helical piles, or driven piers. The choice of foundation depends on soil composition, wind load requirements, and local permitting regulations.
For multi-row arrays, proper spacing prevents shading and allows for maintenance access, including mowing or vegetation control. Optimizing panel tilt and orientation enhances energy production, and some systems offer manual seasonal adjustments for additional performance gains.
Electrical considerations include longer wiring runs, which may require larger-gauge wiring to minimize voltage drop. Proper grounding and bonding are also crucial to meet safety codes.
Pole-Mounted Ground Mounts
Pole-mounted ground mount solar systems use one or more central poles, making them ideal for uneven terrain. However, they often require deeper foundations and must meet wind load and soil stability criteria, which can increase permitting complexity.
Many pole-mounted systems integrate single- or dual-axis solar tracking to enhance energy generation. While solar trackers improve efficiency, they involve moving parts that require regular maintenance. Ensure that customers understand the maintenance demands and that the selected tracker is reliable and backed by strong manufacturer warranties.
Permitting requirements may necessitate engineering reviews to confirm foundation integrity, particularly in areas with high wind or frost depth considerations.
Solar Carports
Solar carport structures provide a dual-function solution by sheltering vehicles while generating solar power. They optimize land use by utilizing otherwise unused space and are especially beneficial in urban or suburban settings with limited ground space for standard solar arrays.
Engineering a ground mount solar design for carports requires accounting for structural integrity, snow and wind loads, and electrical interconnection requirements. Elevated racking means heavier loads on support structures, and wiring runs must be carefully planned to avoid excessive voltage drop.
Ground Mounted Solar Panel Installations
Ground mount solar design requires careful planning to ensure compliance with local permitting regulations, soil conditions, and interconnection standards. Site-specific considerations—such as terrain, wind loads, shading, and utility constraints—affect installation complexity, material selection, and overall project costs. Proper engineering assessments help determine the most effective racking system, foundation type, and electrical layout for long-term system stability and performance.
Installing Standard Mounted Solar Panels
Foundation selection is a critical step in ground mount solar design and is influenced by soil testing, local building codes, and environmental conditions. The most common foundation options include:
-
Concrete piers – A widely used and highly durable option, offering excellent structural stability. However, installation requires excavation, formwork, and curing time, making it more labor-intensive and costly.
-
Helical piles – Ideal for sites with loose, unstable, or rocky soil. These steel screw-like piles are drilled into the ground, providing strong load-bearing capacity with minimal site disturbance.
-
Driven piers – A cost-effective and efficient solution for stable soil conditions, allowing for rapid installation with hydraulic or pneumatic equipment. However, soil analysis is essential to confirm suitability.
-
Ballasted systems – Best suited for locations where ground penetration is not permitted or practical, such as brownfields or capped landfills. These systems use weighted concrete blocks to secure the racking structure but may require additional structural analysis due to wind uplift forces.
In addition to selecting the right foundation, installers must account for row spacing and potential shading issues between panel rows. Proper clearance is necessary to allow for vegetation management and maintenance access.
Some municipalities require security fencing around ground mounted solar panels, which adds cost and complexity. If fencing is needed, careful placement is essential to prevent shading while maintaining access for servicing the system.
Installing Pole-Mounted Solar Panels
Pole-mounted systems require precise engineering to handle structural loads, wind resistance, and soil conditions. These systems often use reinforced concrete foundations or deep-driven piers to ensure stability, particularly in areas prone to high winds or frost heave.
The installation process involves:
-
Site excavation – Augers or specialized drilling equipment may be necessary for digging deep foundation holes, especially in rocky, clay-heavy, or sandy terrain.
-
Structural engineering assessments – Wind loading calculations determine the pole height, foundation depth, and required reinforcement.
-
Electrical layout planning – Since pole-mounted systems are often positioned further from the main electrical panel, careful planning is needed to minimize voltage drop and energy losses. Larger conduit sizing, direct burial cables, or trenching for underground conduit runs may be required.
Tracking systems, commonly paired with pole-mounted arrays, introduce additional engineering challenges. Single-axis and dual-axis trackers enhance energy production but involve moving parts that require regular maintenance. Proper load distribution and manufacturer reliability are key factors when selecting a tracking system.
By leveraging the right engineering expertise, selecting the optimal mounting system, and addressing site-specific constraints, ground mount solar installations can deliver long-term performance and durability.
Pros And Cons Of Ground Mounted Solar Panels
Ground mount solar design offers homeowners an alternative to roof-mounted systems, with several advantages and challenges. The feasibility of ground mounted solar panels depends on site conditions, installation costs, and available yard space.
Pros of Solar Ground Mounts
Ground mounted solar panels offer several advantages over rooftop systems, particularly in terms of energy optimization and installation flexibility. By eliminating roof constraints, these systems can maximize solar exposure, improve efficiency, and integrate advanced technologies like bifacial panels and solar tracking.
One of the most significant advantages of ground mount solar is that it eliminates the need for roof penetrations, which can be a concern for homeowners. Roof-mounted systems require lag bolts and flashing to secure solar racking, potentially affecting roofing warranties or increasing the risk of leaks. With ground mounted solar panels, all racking and structural components are installed independently on the ground, avoiding these concerns.
✅ Optimized Energy Production
Ground mount solar design allows for optimal tilt and azimuth positioning, ensuring maximum solar exposure throughout the year. Unlike roof-mounted systems, which are constrained by roof orientation and slope, ground installations can be placed at the most efficient angle for solar generation.
Additionally, homeowners in regions with heavy snow accumulation can benefit from adjustable-tilt ground mount systems, which can be set to a steeper angle in winter to shed snow and maximize energy capture. The integration of single-axis or dual-axis tracking systems can further boost energy yield by automatically adjusting panel orientation to follow the sun’s path.
✅ Bifacial Solar Panel Compatibility
Ground mounted solar panels can incorporate bifacial solar modules, which generate electricity from both the front and rear sides by capturing reflected sunlight from the ground. This is particularly beneficial when installing panels over light-colored surfaces such as gravel or sand, which enhance albedo effects and improve system efficiency.
✅ Reduced Rapid Shutdown Requirements
The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates rapid shutdown compliance for rooftop solar systems to minimize the risk of electrical hazards to first responders. Ground mount solar installations, particularly those with inverters located near the array, may not be subject to the same stringent rapid shutdown regulations. However, specific requirements depend on local codes and the proximity of electrical components to habitable structures. Homeowners should consult a licensed solar installer to determine compliance requirements in their jurisdiction.
Cons of Solar Ground Mounts
Despite their benefits, ground mount solar systems come with added costs, space requirements, and maintenance considerations. Homeowners must account for higher installation expenses, zoning restrictions, and ongoing vegetation management to ensure long-term performance.
❌Higher Installation Costs
Ground mount solar design often involves higher upfront costs compared to rooftop installations. These additional expenses stem from:
-
Foundation and racking materials – Ground-mounted systems require structural support, such as concrete piers, helical piles, or ballasted foundations, increasing material and labor costs.
-
Permitting and engineering requirements – Many jurisdictions mandate geotechnical analysis and wind-load assessments to ensure structural integrity.
-
Trenching and electrical wiring – Unlike rooftop solar, which typically connects directly to a nearby service panel, ground-mounted arrays may require trenching for conduit runs, increasing labor and material expenses.
❌ Land Use Considerations
Ground mounted solar panels require dedicated yard space, making them less practical for homeowners with limited property size. Additionally, zoning restrictions and homeowners’ association (HOA) regulations may limit the placement of ground mount solar systems, particularly in densely populated areas.
One way to mitigate land use concerns is by integrating solar structures into existing outdoor spaces. For example, solar carports, pergolas, or trellises provide both shade and energy production while reducing overall footprint.
❌ Vegetation Management
Shading from trees, tall grass, or shrubs can significantly reduce solar panel efficiency. Unlike rooftop systems, which are typically elevated above vegetation, ground mounted solar panels require ongoing maintenance to prevent shading-related losses.
Homeowners should plan for:
-
Regular mowing or trimming – Overgrown grass or weeds can cast shadows on lower panels, reducing energy output.
-
Site selection adjustments – Arrays should be positioned away from tree lines or structures that could obstruct sunlight during peak production hours.
Are PE stamps required for permitting a pole-mounted ground mount solar system?
The requirement for a Professional Engineer (PE) stamp when permitting a pole-mounted ground mount solar system depends on local building codes and structural engineering regulations. Many jurisdictions mandate a PE stamp for ground mount solar designs involving structural components, such as pole-mounted systems, due to wind load, soil stability, and foundation requirements.
A PE stamp verifies that the ground mounted solar panel system complies with engineering best practices and safety standards. This certification ensures the system is designed to withstand environmental factors, such as high winds and seismic activity, based on site-specific conditions. To determine if a PE stamp is required, homeowners should consult local permitting offices and review applicable building codes.
GreenLancer specializes in solar engineering reviews and provides access to licensed Professional Engineers in all 50 states to streamline the permitting process for ground mount solar installations.
Rooftop Vs. Ground Mounted Solar Panels
Choosing between rooftop solar panels and a ground mount solar system is a crucial decision for homeowners considering solar energy. Each option has unique benefits and potential challenges based on site conditions, energy goals, and installation costs.
Ground-mounted solar panels offer greater flexibility in system size, orientation, and efficiency. They can be installed at the optimal tilt and azimuth for maximum energy production, making them a strong choice for properties with adequate space. However, they require additional permitting, site preparation, and potential structural engineering approvals.
Rooftop solar panels integrate seamlessly with a home’s structure, minimizing land use while often reducing installation costs. Yet, roof-mounted systems are constrained by the home’s roof orientation, available space, and structural integrity.
Navigating ground mount solar design and engineering challenges shouldn’t be a barrier to installation. GreenLancer’s network of solar design and engineering professionals provides expert solutions for ground-mounted solar panel systems.
Connect with a GreenLancer representative today to streamline your solar project! Complete the form below to get started.
Source link